
by dnshah | Jul 28, 2020 | Age Defying, Health and Wellness Tips, Virus
What we know for sure is that smoking seems to increases risk of flu. Data shows a higher mortality among smokers in the 2012 MERS-CoV. Some preliminary studies on COVID19 and smokers found unfavorable outcomes. This data was done so early with COVID19, that it may not be current but I wanted to provide the analysis and observations.
- Smokers were 1.4 times more likely to have severe symptoms compared to non-smokers
- Smokers were 2.4 times more likely to be admitted to an ICU, need mechanical ventilators, or die compared to non-smokers
The pattern (this study and more current ones) seems to indicate that smoking is most likely linked to negative progression and adverse outcomes with the COVID19 pandemic. So, this is more evidence to indicate that one of the best things smokers can do to protect themselves from COVID19 risks is to quit smoking.
Although this habit is one of the harder habits to break, please reach out and get help from medical professionals or work with a health & wellness coach trained in this to progress your goal of smoking cessation. It’s a life-saving lifestyle change.

by dnshah | Jul 28, 2020 | Age Defying, Diet and Weight Loss, Health and Wellness Tips, Virus
Green tea contains an anti-viral and anti-inflammatory compound called EGCG (epigallocatechin). Some of the benefits of EGCG that we know about include:
- Direct or Indirect Inhibition of viral entry: (hepatitis B & C, Zika, HSV, HPV, Epstein-Barr, Dengue, West Nile, Chikunjunya, Enterovirus, Japanese Encephalitis, Tick born Encephalitis, HIV, Ebola, Influenza)
- Inhibits inflammatory enzymes
- Helps to Prevent respiratory infection
At this time COVID19 has no known universally accepted treatment or cure and there is no clinical evidence that EGCG can prevent, treat, or cure COVID19. Still some chemists are looking into the impact of EGCG on Covid19 because it has a high affinity for binding to the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
While primarily found in green tea, small amounts can also be sourced from apples, kiwi, strawberries, hazelnuts, and pecans. There were some concerns cited on the purity of green teas sourced internationally, and possible harm from teas sourced from sites that didn’t have as thorough government safety standards.
The full effects of EGCG on COVID19 are unknown to date. Excessive EGCG hasn’t shown serious adverse effects in studies ()19). It seems to have broad human appeal due its safety profile; however excessive caffeine consumption should be monitored. There are known medication interactions so always check with your doctor before making dietary changes.

by dnshah | Jul 28, 2020 | Age Defying, Diet and Weight Loss, Health and Wellness Tips, Virus
Dietary flavonoids are a large family of plant compounds sharing a structure, and there are 6 major subfamilies (anthocyanidins, flavan-3-ols, flavanones, flavones, flavonols, and isoflavones). Quercetin is a flavonoid from the Flavanol subfamily.
Some of the functions quercetin provides (human or animal studies) include:
Main dietary sources (from the USDA database) are listed below. The way food is prepared (boiled, fried, etc.) impacts quercetin concentration.
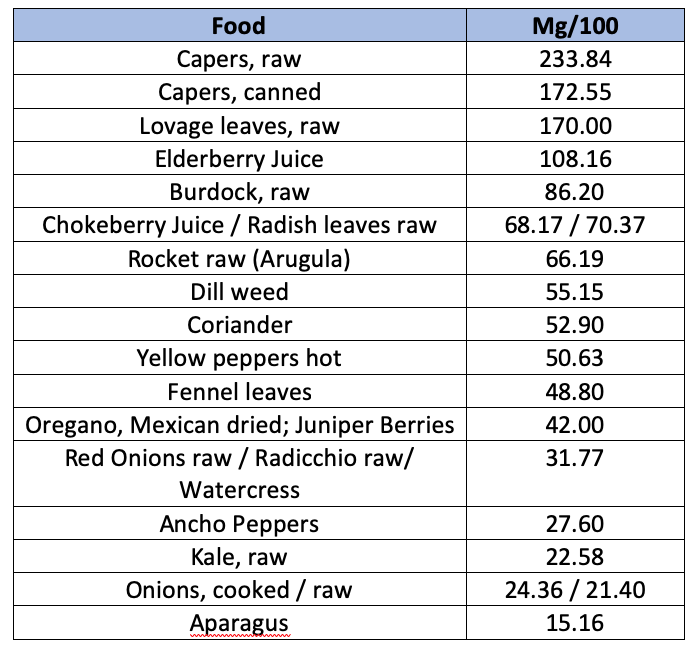
Excessive quercetin may cause headache, tingling of arms/legs, and kidney damage. There are some possible medication interactions (antibiotics, cyclosporine, warfarin, liver medications), so always consult a doctor when changing dietary habits.

by dnshah | Jul 28, 2020 | Age Defying, Diet and Weight Loss, Health and Wellness Tips, Stress Management, Virus
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that isn’t present in many foods. One of the ways we synthesize vitamin D is through sunlight on our skin. Many factors will control how much vitaminD our bodies can make (think location, altitude, season, skin darkness), so it is important to have a backup vitamin D strategy, especially in winters when we don’t have as much opportunity to be in the sun outdoors. Darker skin reduces the absorption of vitamin D.
Vitamin D is very important for our immune system to run optimally. Some of its functions include:
- Stimulate lung protection from infection; reduces risk of acute respiratory infection
- Inflammation reduction
- Helps with calcium absorption (promotes healthy bones)
- Modulation of cell growth (including apoptosis)
- Neuromuscular functions
- Helps to prevent colon, prostate, and breast cancers
There are no known studies proving prevention, reduction, treatment, or a cure against COVID19. That said, many scientists are talking about ensuring adequate vitamin D especially now in light of pandemic conditions.
According to the USDA, adults and children (1-70 years) need 600 IU of vitamin D daily, with older adults needing 800 IU daily. This vitamin is not easily found in foods, but below are some food sources. Non-food sources include sunlight and supplements.
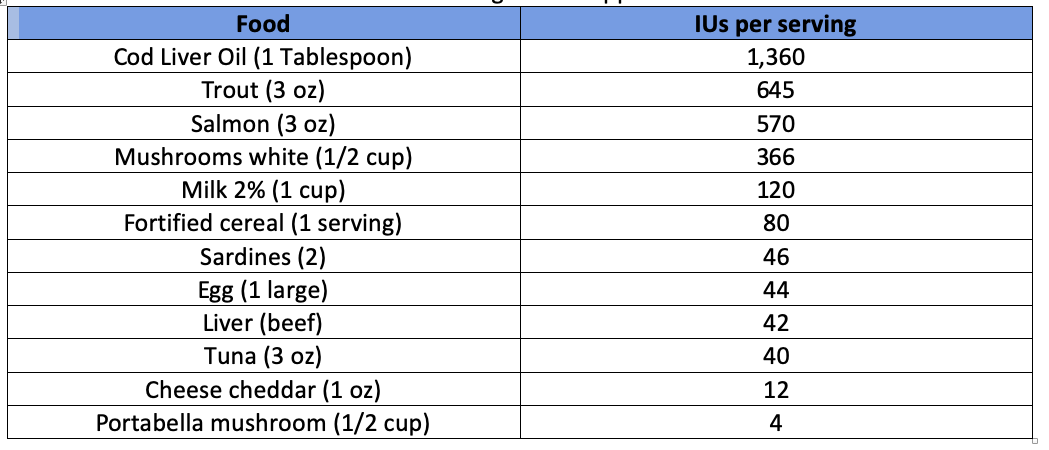
Obtaining sufficient vitamin D from food alone is difficult, hence the need to fortify staple foods with vitamin D (milk, cereals, orange juice, yogurts, margarines). If people have fat absorption issues, this can reduce the uptake of vitamin D also. Many people depend upon vitamin D supplementation to meet the recommended daily intakes.
With supplementation, there can be potential interactions with medications (steroids, weight loss medications) and risks that come with getting too much vitamin D. Excessive vitamin D can cause symptoms (anorexia, weight loss, heart arrhythmias, excessive calcium-blood levels). Excessive calcium-blood levels can lead to vascular and tissue calcification along with other damages.

by dnshah | Jul 28, 2020 | Age Defying, Diet and Weight Loss, Health and Wellness Tips, Virus
Vitamin C is essential water-soluble vitamin; our bodies don’t make it so we have to get a new supply daily. In general It protects us from oxidative stress, the normal “wear and tear” process of living. Some other functions of vitamin C include the following(1):
- Maintaining our epithelial barriers – which means it protects us from the outside world (think COVID19 virus and other pathogens, and leaky gut – aka intestinal permeability)
- Our immune natural killer (NK) cells depend upon vitamin C for their optimal function and movements as they travel through the body protecting us from foreign invaders.
- Our immune macrophages depend upon vitamin C for their optimal function as they travel through the body cleaning up debris – “taking out the trash” to minimize inflammatory responses.
- Our immune T- and B- cells depend upon vitamin C for their optimal function as they target microbial killing to defend our bodies.
While there are NO known clinical trials using vitamin C for preventing or treating or curing COVID19, China is actively doing a clinical trial concluding in Sept, 2020 with it.(7)
The important factor with vitamin C is that since our bodies don’t make it, we must come up with a regular routine of supplying the body with good doses daily. And then we have to ensure our digestion is running optimally so we can absorb the nutrients we need. According to USDA, the daily recommended intake for vitamin C for adults is 75mg (females) or 90mg (males) and much lower for babies and children. Sufferers of malabsorption, macular degeneration, certain diseases, and smokers would need more. Some great food sources include:
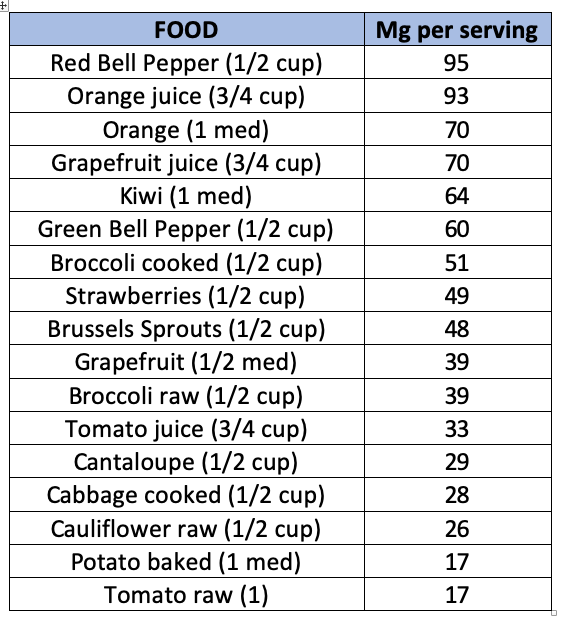
There are minimal health risks from excessive vitamin C (GI issues), however there may be medication interactions with vitamin C supplements. Vitamin C and other antioxidant use while undergoing cancer treatment is controversial at this time. Always seek the help from your doctor before making dietary changes.

by dnshah | Jul 1, 2020 | Age Defying, Diet and Weight Loss, Health and Wellness Tips, Obesity, Stress Management
Ketogenic diets are the current trend, and people want to learn more about which fats are better for you compared to others. While I’m not a BIG believer of long-term ketogenesis, I have seen that the body performs well during ketogenesis; and I know that keto diets work for short-term weight-loss. And I love when bodies are in a fat-burning mode, because healthy fats are REALLY where it’s at for optimally fueling our brains.
Many decades ago I remember my teenage-self making a weight loss goal, and deciding I needed to cut down on fats. I declared to my family, “no more ghee!” Ghee is a clarified butter (healthy fat) made by heating butter and removing the milk solids. It’s better tolerated because it removes the lactose and casein. Its origin is India, so what I had just announced did not bode well for my Indian household. My grandmother looked up at me and promptly informed me that was a bad idea for my bones and brain. Not seeing any logic to how a little fat in a food was going to help my bones or my brain, I explained to her the western science of cutting down fat to lose weight. My grandmother laughed at me and explained the eastern science of ensuring adequate healthy fats in the body to “lubricate” the bones and brain. I didn’t understand nor believe her… after all I was the SCIENTIST! Fast forward decades, and it turns out… grandma was right! It’s really important to consume healthy fats like ghee for fueling our brains and bones, as well as our skin, hair, and digestion. Today Western science has trials underway to better understand the benefits of healthy fats (especially ghee vs. coconut oil). Ghee contains vitamin K2 which is important for calcium absorption and bone strengthening; and it’s also a great skin moisturizer.
Coconut oil has also been BIG since keto diets have trended and especially after Bulletproof Coffee hit mainframe America. People want their MCTs (medium chain triglycerides) and coconut oil has them! MCTs are the key to getting the body into ketosis, and known for improving brain health, decreasing insulin resistance, decreasing inflammation, and promoting weight loss. And it has unofficially been reported that coconut oil has some benefits regarding Alzheimer’s, Dementia, heart disease, diabetes, autoimmunity, and cancer.
The question that logically comes next is… which fat is better? As an adult woman I’m not going to disrespect ghee (like I did as a teenager). Both coconut oil and ghee have a lot going for them in terms of healthy fat advantages, but both have distinct nutrient profiles.
- One of the main fuels for building cells in the intestine is Butyric Acid. It’s also important for digestive health, decreasing inflammation, and improving IBS issues. Butyric acid is abundant in ghee, and not found in coconut oil.
- MCTs benefit our gut microbiome, so can improve overall digestion. Coconut oil contains 60% MCTs and ghee is 25% MCTs.
So coconut oil may be a better fat for brain health, but ghee seems to be a better fat for digestive health. So it depends upon which goal you desire more. Or… you could combine both the ghee and coconut oil and get BOTH benefits! Some health food stores have already mixed both and offer them together.
Current food specialists warn about the consumption of excessive saturated fats. Both ghee and coconut oil fall into this category. So before changing your diet and lifestyle, always talk to your health practitioner or integrative physician and ensure there are no issues or contraindications with the desired change.











