Dietary flavonoids are a large family of plant compounds sharing a structure, and there are 6 major subfamilies (anthocyanidins, flavan-3-ols, flavanones, flavones, flavonols, and isoflavones). Quercetin is a flavonoid from the Flavanol subfamily.
Some of the functions quercetin provides (human or animal studies) include:
- Neutralizes oxidative damage (antioxidant properties)
- Anti-inflammatory properties
- Regulates immunity
- Inhibits cells from viral infections
- Reduce upper respiratory tract infection severity in older adults (23)
Main dietary sources (from the USDA database) are listed below. The way food is prepared (boiled, fried, etc.) impacts quercetin concentration.
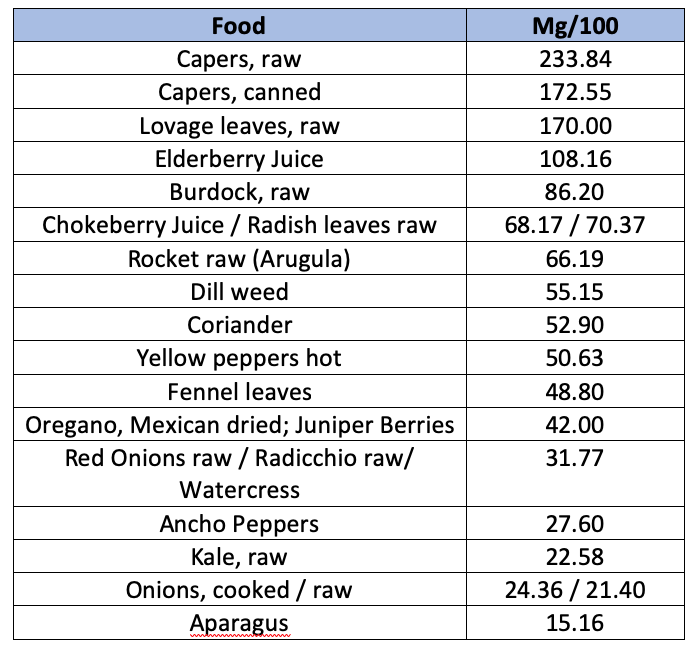
Excessive quercetin may cause headache, tingling of arms/legs, and kidney damage. There are some possible medication interactions (antibiotics, cyclosporine, warfarin, liver medications), so always consult a doctor when changing dietary habits.



